Activities of U.S. Affiliates of Foreign Multinational Enterprises in 2020
The U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) recently released statistics on the 2020 activities of U.S. affiliates of foreign multinational enterprises (MNEs). These statistics provide a picture of the overall activities of U.S. affiliates of foreign parents and contain a wide variety of indicators of their financial structure and operations. The statistics cover items that are needed to analyze the characteristics, performance, and economic impact of foreign-owned businesses on the U.S. economy and are obtained from mandatory surveys of U.S. affiliates conducted by BEA.
The following charts present highlights of BEA's U.S. affiliate statistics for 2020. Much more detail, including additional data items, can be found on BEA's website.
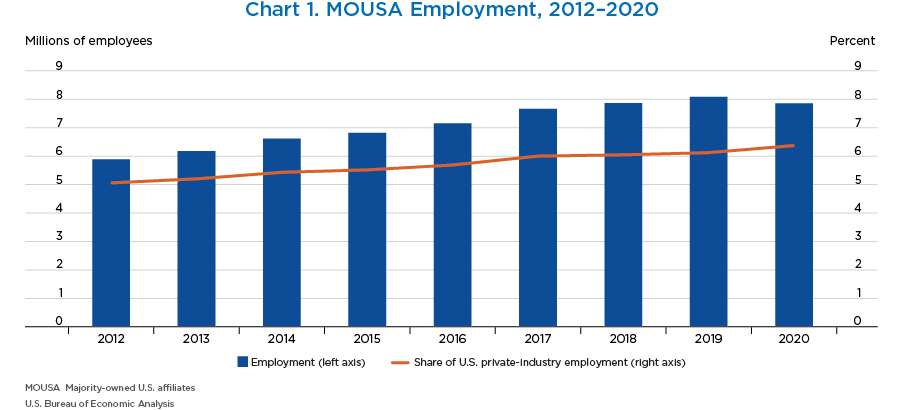
- MOUSAs of foreign MNEs employed 7.86 million workers in the United States in 2020, 2.8 percent less than in 2019.
- MOUSAs accounted for 6.4 percent of total private-industry employment in the United States, up from 6.1 percent in 2019, as total private-industry employment fell more than MOUSA employment.
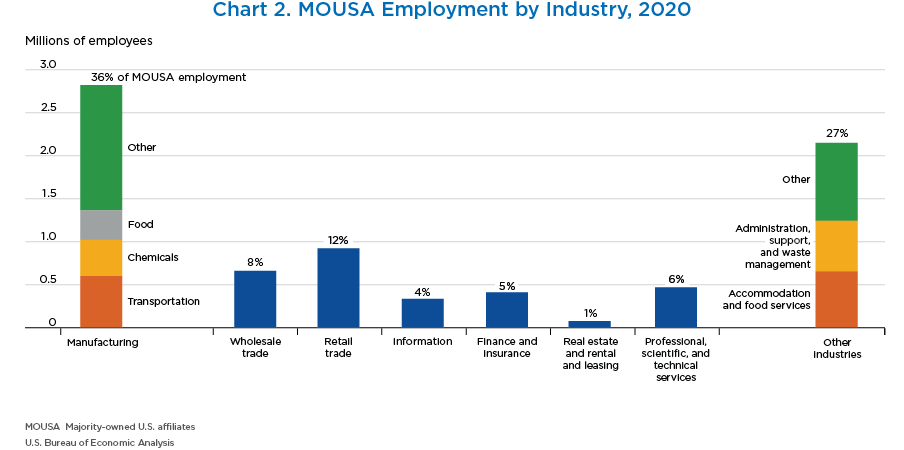
- The manufacturing sector accounted for 36 percent of MOUSA employment. Within manufacturing, transportation equipment employed the most workers, followed by chemicals and food.
- Within other industries, accommodation and food services, along with administration, support, and waste management, employed the most workers.
- Employment decreased in all major industry categories with the exception of professional, scientific, and technical services.
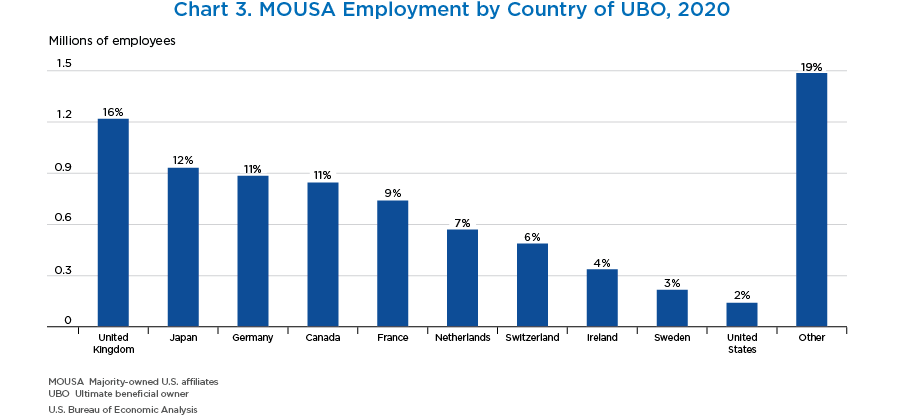
- By country of UBO, the United Kingdom, Japan, Germany, Canada, and France accounted for the largest share of MOUSA employment. These five countries accounted for 59 percent of all MOUSA employment.
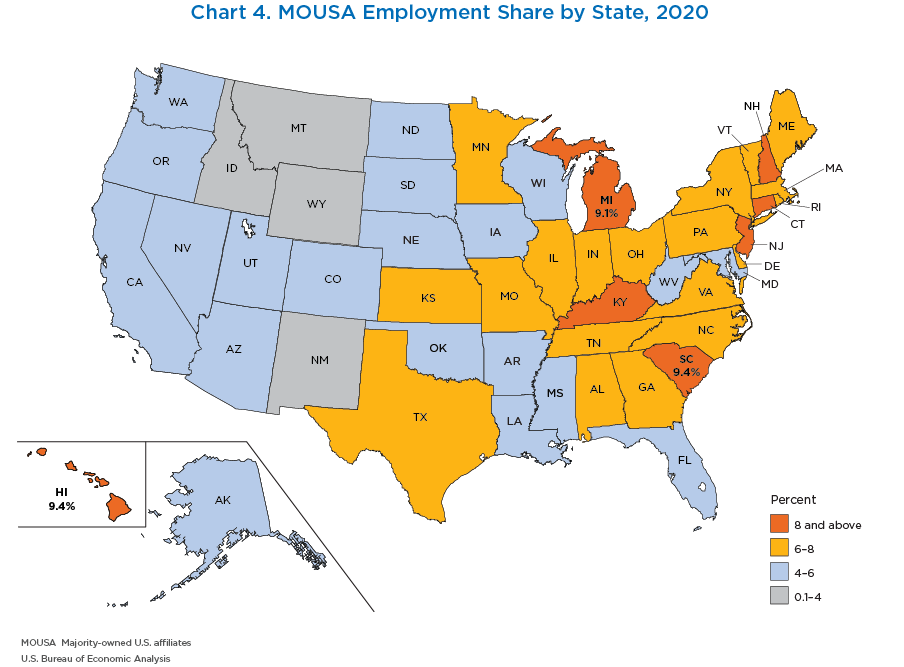
- By state, the share of private-industry employment accounted for by MOUSAs was highest in South Carolina (9.4 percent), Hawaii (9.4 percent), and Michigan (9.1 percent). In South Carolina and Michigan, MOUSAs in the manufacturing sector employed the most workers, while “other industries,” primarily accommodation and food services, employed the most MOUSA workers in Hawaii.
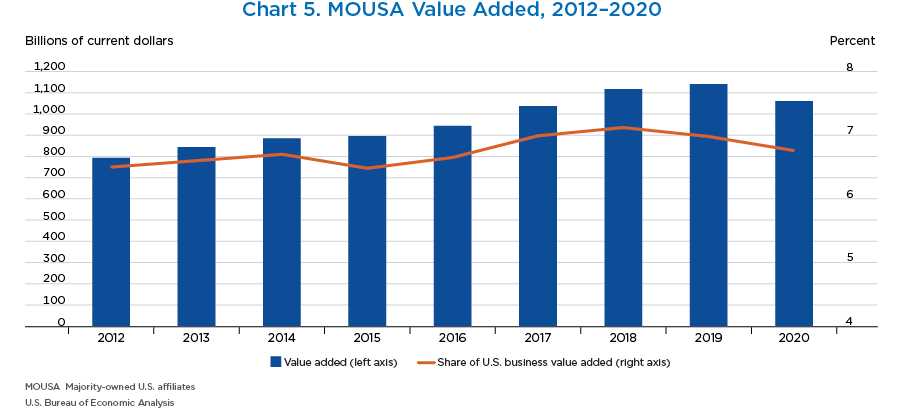
- Current-dollar value added of MOUSAs decreased 7.0 percent to $1.1 trillion in 2020.
- MOUSAs accounted for 6.8 percent of total U.S. business-sector value added, down from 7.0 percent in 2019.
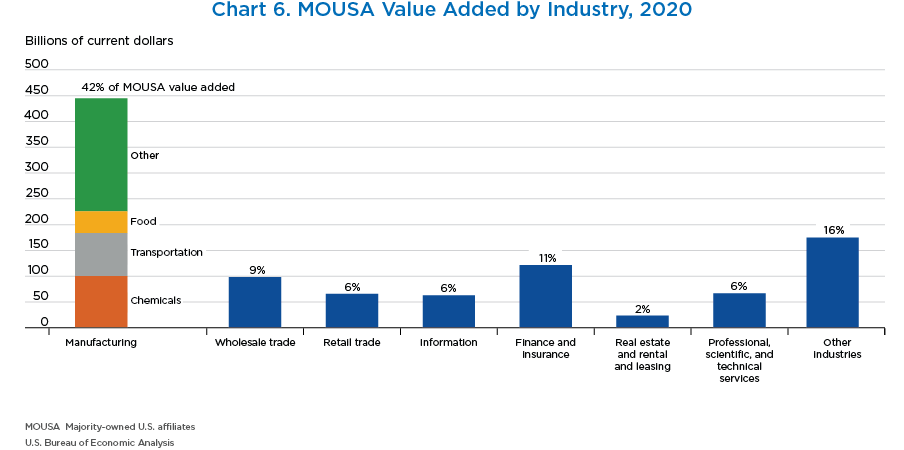
- Manufacturing accounted for most of MOUSA value added. The largest industry within manufacturing was chemicals (which includes pharmaceuticals), followed by transportation equipment.
- Other industries and finance and insurance were the next largest contributors to MOUSA value added.
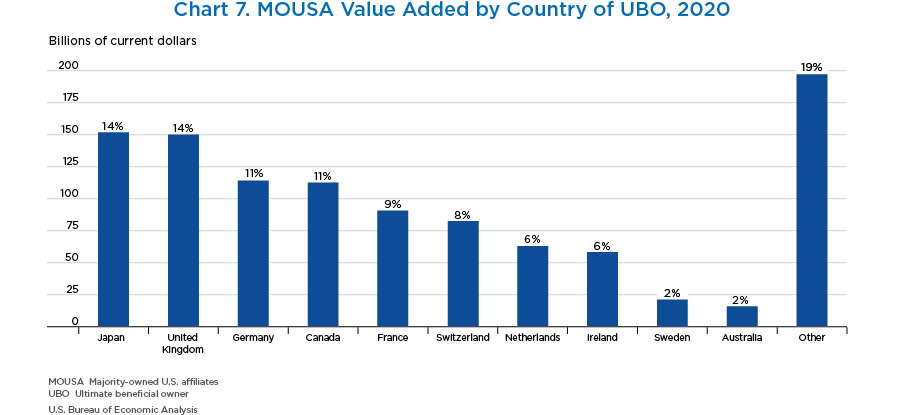
- By country of UBO, Japan, the United Kingdom, Germany, Canada, and France accounted for the largest share of MOUSA value added. Like employment, these five countries accounted for 59 percent of all MOUSA value added.
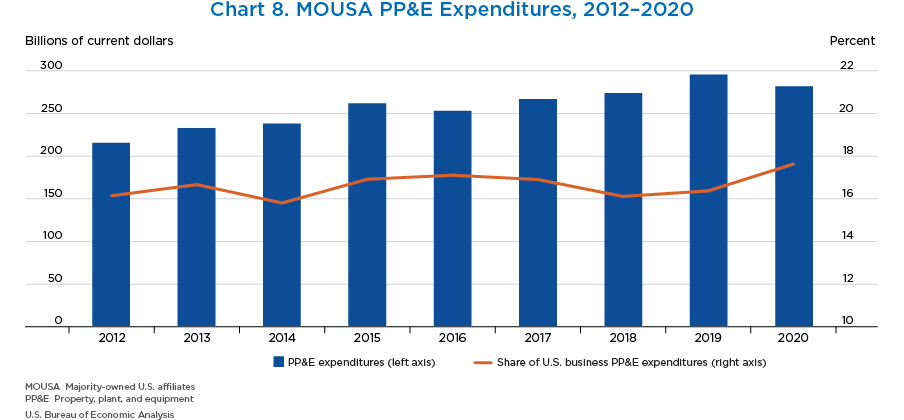
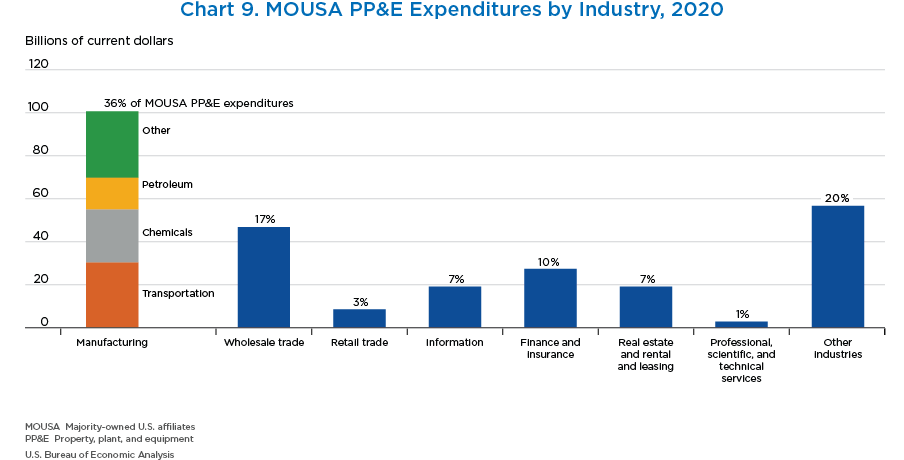
- Expenditures for property, plant, and equipment (PP&E) by MOUSAs decreased 4.7 percent to $281.8 billion in 2020. By industry, there were significant offsetting increases and decreases.
- MOUSAs accounted for 17.6 percent of total U.S. private business capital expenditures, which is substantially higher than employment and value-added shares.
- Manufacturing accounted for 36 percent of MOUSA PP&E expenditures. Within manufacturing, the largest contributor was transportation equipment, followed by chemicals.
- Within other industries, utilities and mining accounted for the largest shares.
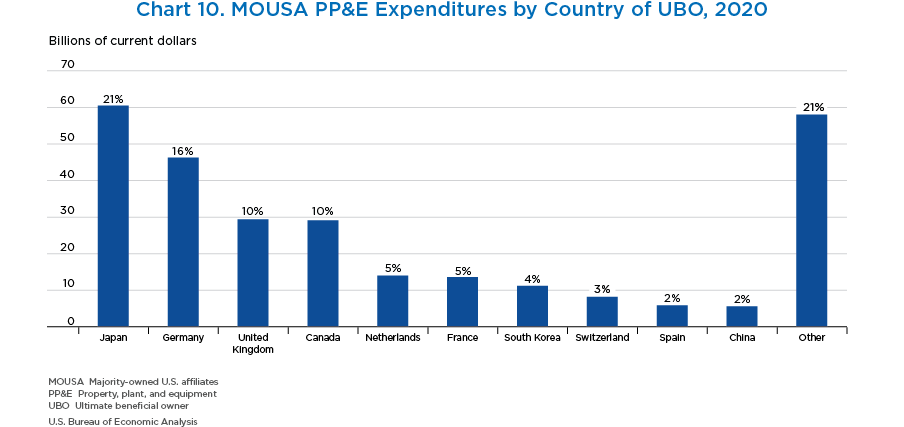
- By country of UBO, Japan, Germany, the United Kingdom, Canada, and the Netherlands accounted for the largest share of MOUSA PP&E expenditures. PP&E expenditures are slightly more concentrated by country than employment and value added, with the top five countries of UBO accounting for 64 percent of MOUSA PP&E expenditures.
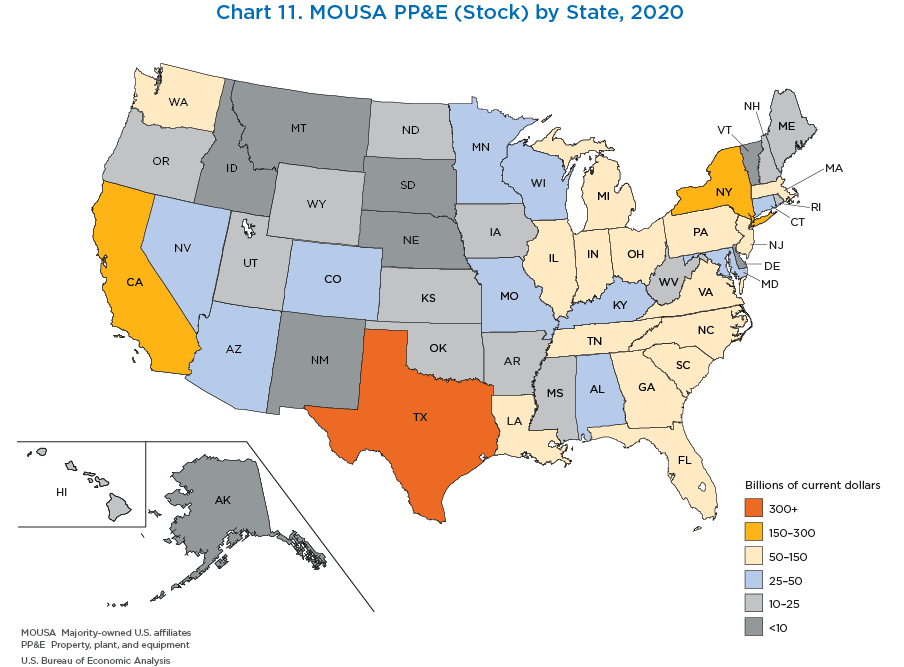
- The preceding charts illustrate PP&E expenditures. BEA also collects detail on gross PP&E stock, which is the value of all land, property, plant, and equipment before accumulated depreciation. These data can be used as a proxy for state-level foreign direct investment levels that are not available in BEA's direct investment position statistics.
- Total gross PP&E for the United States was $2.9 trillion. The states with the largest share of MOUSA gross PP&E were Texas ($451 billion), California ($249 billion), and New York ($223 billion). Alaska saw the largest gross PPE decrease of $24.7 billion. New York saw the largest gross PPE increase of $11.9 billion.
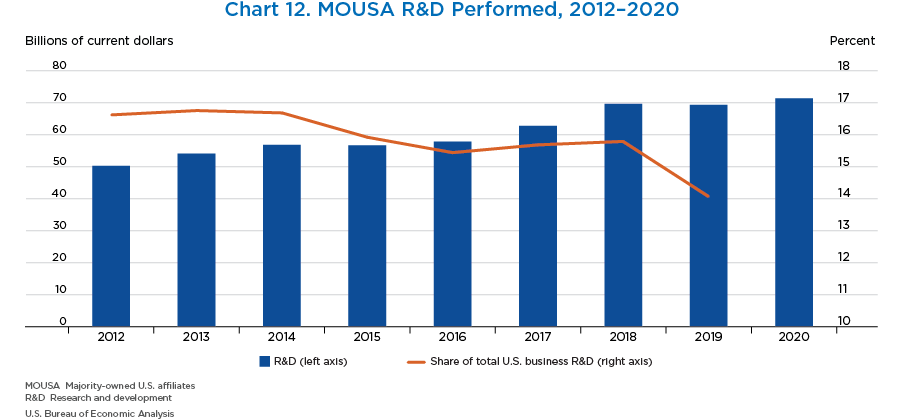
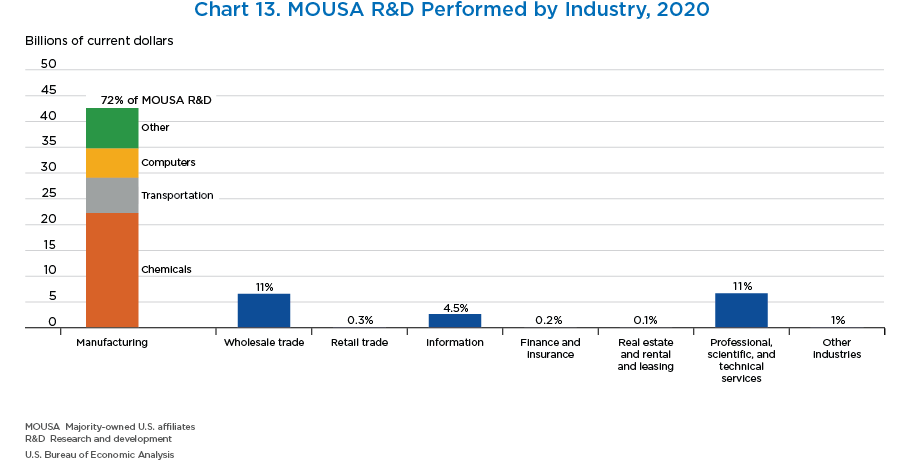
- Research and development (R&D) performed by MOUSAs increased 3.0 percent to $71.4 billion in 2020.
- MOUSAs accounted for 14.1 percent of total U.S. business R&D in 2019, the latest year that U.S business R&D data is available. This share is larger than the MOUSA share of employment or value added.
- Manufacturing made up the majority of all MOUSA R&D performed, accounting for 72 percent of total R&D. Chemicals manufacturing (which includes pharmaceuticals) accounted for most of MOUSA manufacturing R&D.
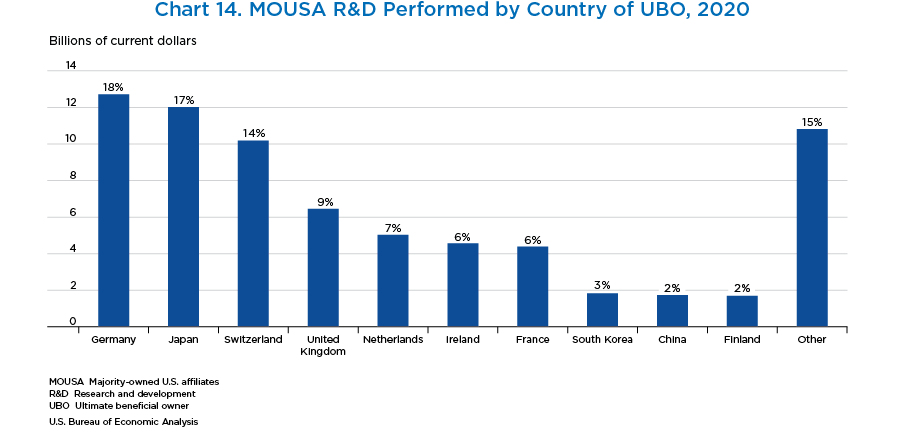
- By country of UBO, Germany, Japan, Switzerland, the United Kingdom, and the Netherlands accounted for the largest share of MOUSA R&D performed. These top five countries of UBO accounted for 65 percent of MOUSA R&D.
- Employment covers the total number of full-time and part-time employees on the payroll at the end of the year.
- Value added is the value of the final goods and services produced by a firm's labor and property. Value added represents the firm's contribution to U.S. gross domestic product.
- Expenditures for property, plant, and equipment cover expenditures for land and depreciable structures and equipment.
- Research and development (R&D) performed includes expenditures for R&D performed by the U.S. affiliate, whether the R&D was for their own use or for use by others.